4369. Arson
There is an
ordinary spider web in front of you. However, as an experienced competitive
programmer, you immediately notice that it represents a connected graph
with vertices and edges. If some vertex is set on fire,
it ignites immediately; after one second, all vertices adjacent to it will
catch fire, then the vertices adjacent to the already burning ones, and so on.
You are given the
vertices of the web where the fire starts simultaneously. Determine how many
seconds will pass until the last vertex catches fire and also find the number
of that vertex.
Input. The first line contains two positive
integers n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105) and m (n
– 1 ≤ m ≤ 105)
– the number of vertices and the number of edges, respectively.
The next m lines contain pairs
of integers u and
v (1 ≤ u, v ≤ n) denoting vertices connected
by an edge.
The next line contains an integer k
(1 ≤ k ≤ n) – the number of ignition points.
The last line contains k integers
– the indices of the vertices where the fire starts simultaneously.
Output. In the first
line, print the time (in seconds) when the last vertex catches fire. In the
second line, print the number of that vertex. If there are multiple such
vertices, print the one with the smallest index.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
6 6 1 2 2 6 1 5 5 6 3 5 4 5 2 1 2 |
2 3 |
SOLUTION
graphs
- bfs
Algorithm analysis
To solve the problem, it
is necessary to run a breadth-first search from multiple sources. To do this,
place all ignition points into a queue and then start the algorithm.
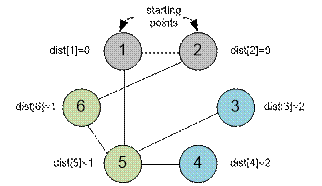
Example
The graph shown in the
example has the following structure:
Algorithm implementation
Declare the arrays.
vector<int> dist;
vector<vector<int> > g;
queue<int> q;
The bfs function performs a breadth-first search. All
sources for this search are preloaded into the queue q.
void bfs(void)
{
while (!q.empty())
{
int v = q.front(); q.pop();
for (int to : g[v])
if (dist[to] == -1)
{
q.push(to);
dist[to] = dist[v] + 1;
}
}
}
The main part of the program. Read the input data. Build the graph.
scanf("%d %d",&n,&m);
g.resize(n+1);
for(i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
scanf("%d
%d",&u,&v);
g[u].push_back(v);
g[v].push_back(u);
}
The array dist[i] stores the time after which vertex i will
catch fire. Initially, all values of dist[i] are set to -1.
dist =
vector<int>(n+1,-1);
Read the numbers of the vertices that serve as ignition points. For each
such vertex id set dist[id] = 0 and add it to the queue.
scanf("%d",&k);
for(i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&id);
dist[id] = 0;
q.push(id);
}
Run the breadth-first search.
bfs();
Let’s find the vertex id that will catch fire last. The variable mx
stores the time after which it will ignite.
mx = -1;
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (dist[i]
> mx)
{
mx = dist[i];
id = i;
}
First, print the value of dist[id] – the time when the last vertex will catch fire. Then, print the number of
the vertex id.
printf("%d\n",dist[id]);
printf("%d\n",id);
Java implementation
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static ArrayList<Integer>[] g;
static Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer>();
static int dist[];
static int n, m;
static void bfs()
{
while(!q.isEmpty())
{
int v = q.poll();
for(int i = 0; i < g[v].size(); i++)
{
int to = g[v].get(i);
if (dist[to] == -1)
{
q.add(to);
dist[to] = dist[v] + 1;
}
}
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
n = con.nextInt(); m = con.nextInt();
g = new ArrayList[n+1];
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
g[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>();
dist = new int[n+1];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int u = con.nextInt();
int v = con.nextInt();
g[u].add(v);
g[v].add(u);
}
Arrays.fill(dist,-1);
int k = con.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
int id = con.nextInt();
dist[id] = 0;
q.add(id);
}
bfs();
int max = -1, id = -1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (dist[i] > max)
{
max = dist[i];
id = i;
}
System.out.println(dist[id]);
System.out.println(id);
con.close();
}
}